WARNING: ADDICTION, ABUSE, AND MISUSE; RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS); LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION; ACCIDENTAL INGESTION; CARDIOVASCULAR (CV) THROMBOTIC EVENTS; GASTROINTESTINAL (GI) BLEEDING, ULCERATION, AND PERFORATION; ULTRA-RAPID METABOLISM OF TRAMADOL AND OTHER RISK FACTORS FOR LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION IN CHILDREN; NEONATAL OPIOID WITHDRAWAL SYNDROME; INTERACTIONS WITH DRUGS AFFECTING CYTOCHROME P450 ISOENZYMES; RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) DEPRESSANTS
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse
SEGLENTIS exposes patients and other users to the risks of opioid addiction, abuse, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death. Assess each patient’s risk prior to prescribing SEGLENTIS and monitor all patients regularly for the development of these behaviors and conditions.
Opioid Analgesic REMS
To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a REMS for these products. Under the requirements of the REMS, drug companies with approved opioid analgesic products must make REMS-compliant education programs available to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers are strongly encouraged to complete a REMS-compliant education program, counsel patients and/or their caregivers, with every prescription, on safe use, serious risks, storage, and disposal of these products, emphasize to patients and their caregivers the importance of reading the Medication Guide every time it is provided by their pharmacist, and consider other tools to improve patient, household, and community safety.
Life-threatening Respiratory Depression
Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression may occur with use of SEGLENTIS. Monitor for respiratory depression, especially during initiation of SEGLENTIS.
Accidental Ingestion
Accidental ingestion of even one dose of SEGLENTIS, especially by children, can be fatal.
CV Thrombotic Events
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in the treatment and may increase with duration of use.
-
SEGLENTIS is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious GI adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious (GI) events.
Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Tramadol and Other Risk Factors for Life-threatening Respiratory Depression in Children
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received tramadol. Some of the reported cases followed tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy; in at least one case, the child had evidence of being an ultra-rapid metabolizer of tramadol due to a CYP2D6 polymorphism. SEGLENTIS is contraindicated in children younger than 12 years of age and in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. Avoid the use of SEGLENTIS in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of tramadol.
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
Prolonged use of SEGLENTIS during pregnancy can result in neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome, which may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts. If opioid use is required for a prolonged period in a pregnant woman, advise the patient of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available.
Interactions with Drugs Affecting Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes
The effects of concomitant use or discontinuation of cytochrome P450 3A4 inducers, 3A4 inhibitors, or 2D6 inhibitors with tramadol are complex. Use of cytochrome P450 3A4 inducers, 3A4 inhibitors, or 2D6 inhibitors with SEGLENTIS requires careful consideration of the effects on the parent drug, tramadol, and the active metabolite, M1.
Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
-
Reserve concomitant prescribing of SEGLENTIS and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
-
Limit treatment to the minimum duration.
-
Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
Indication
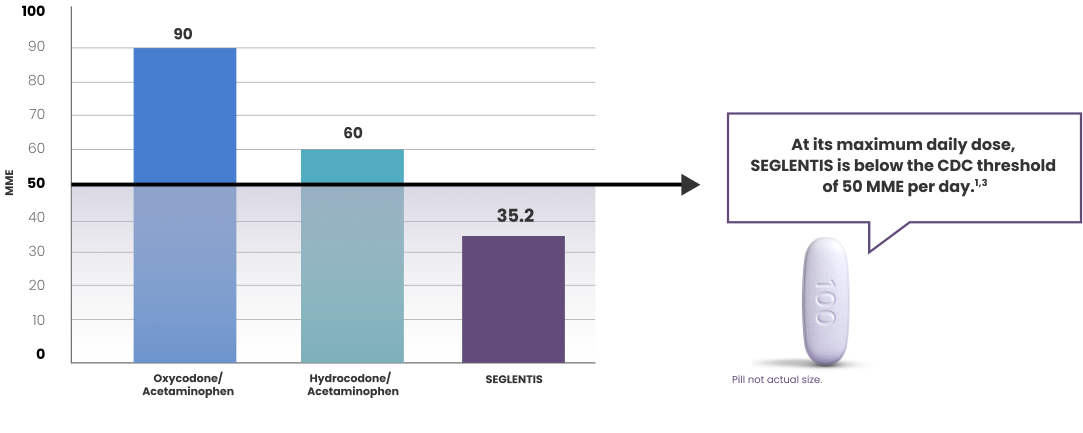
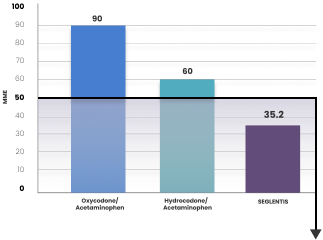
SEGLENTIS contains tramadol hydrochloride, an opioid agonist, and celecoxib, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, and is indicated for the management of acute pain in adults that is severe enough to require an opioid analgesic and for which alternative treatments are inadequate.
Limitations of Use
Because of the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse with opioids, even at recommended doses, reserve SEGLENTIS for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options [e.g., non-opioid analgesics]:
-
Have not been tolerated, or are not expected to be tolerated.
-
Have not provided adequate analgesia, or are not expected to provide adequate analgesia.
Contraindications
-
Children younger than 12 years of age.
-
Postoperative management in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy.
-
Significant respiratory depression.
-
In the setting of CABG surgery.
-
Acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in absence of resuscitative equipment.
-
Known or suspected GI obstruction, including paralytic ileus.
-
Hypersensitivity to tramadol, celecoxib, any other component of this product, or sulfonamides, or opioids.
-
Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use of MAOIs within the last 14 days.
-
History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs.
Warnings and Precautions
-
Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse: Although the risk of addiction in any individual is unknown, it can occur in patients appropriately prescribed SEGLENTIS. Addiction can occur at recommended dosages and if the drug is misused or abused.
-
Life-threatening Respiratory Depression: Serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression has been reported with the use of opioids, even when used as recommended. Respiratory depression, if not immediately recognized and treated, may lead to respiratory arrest and death. Management of respiratory depression may include close observation, supportive measures, and use of opioid antagonists, depending on the patient’s clinical status. Carbon dioxide (CO2) retention from opioid-induced respiratory depression can exacerbate the sedating effects of opioids. While serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression can occur at any time during the use of SEGLENTIS, the risk is greatest during the initiation of therapy. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression, especially within the first 24-72 hours of initiating therapy with SEGLENTIS. Consider prescribing naloxone, based on the patient’s risk factors for overdose, such as concomitant use of CNS depressants, a history of opioid use disorder, or prior opioid overdose.
-
CV Thrombotic Events: To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use SEGLENTIS for the shortest duration possible. Avoid the use of SEGLENTIS in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. If SEGLENTIS is used in patients with a recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia.
-
GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation: Use the approved dosage for the shortest possible duration.
-
Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Tramadol and Other Risk Factors for Life-threatening Respiratory Depression in Children: Even at labeled dosage regimens, individuals who are ultra-rapid metabolizers may have life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression or experience signs of overdose (such as extreme sleepiness, confusion, or shallow breathing). Therefore, individuals who are ultra-rapid metabolizers should not use SEGLENTIS.
-
Risk from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants: Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of SEGLENTIS with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (e.g., non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, alcohol). Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. If the decision is made to prescribe a benzodiazepine or other CNS depressant concomitantly with an opioid analgesic, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use.
-
Serotonin Syndrome Risk: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported with the use of tramadol, a component of SEGLENTIS, particularly during concomitant use with serotonergic drugs. Serotonergic drugs include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), certain muscle relaxants (i.e., cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone), and drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (including MAOls, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue). This may occur within the recommended dosage range. The onset of symptoms generally occurs within several hours to a few days of concomitant use but may occur later than that. Discontinue SEGLENTIS if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
-
Increased Risk of Seizure: Can occur at the recommended dose of tramadol. Concomitant use of SEGLENTIS increases the seizure risk in patients taking: SSRIs and SNRIs, antidepressants or anorectics, TCAs, and other tricyclic compounds (e.g., cyclobenzaprine, promethazine, etc.), other opioids, MAOls, neuroleptics, or other drugs that reduce the seizure threshold. Risk may increase in patients with epilepsy, a history of seizures, and in patients with a recognized risk for seizures.
-
Suicide Risk: Prescribe SEGLENTIS with caution for patients with a history of misuse and/or who are currently taking CNS-active drugs including tranquilizers, or antidepressant drugs, alcohol in excess, and patients who suffer from emotional disturbance or depression.
-
Adrenal Insufficiency: Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than one month of use. Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible. If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to allow adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function recovers. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency. The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency.
-
Life-threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: SEGLENTIS-treated patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale, and those with a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia, hypercapnia, or pre-existing respiratory depression, are at increased risk of decreased respiratory drive including apnea, even at the recommended dosage of SEGLENTIS.
Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients
Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients because they may have altered pharmacokinetics, or altered clearance, compared to younger, healthier patients.
Monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating SEGLENTIS and when SEGLENTIS is given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration.
-
Severe Hypotension: Tramadol, a component of SEGLENTIS, may cause severe hypotension including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administration of certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics). Monitor these patients for signs of hypotension after initiating dosage of SEGLENTIS. In patients with circulatory shock, tramadol may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. Avoid the use of SEGLENTIS in patients with circulatory shock.
-
Risks of Use in Patients with Increased Intracranial Pressure, Brain Tumors, Head Injury, or Impaired Consciousness: In patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention (e.g., those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors), SEGLENTIS may reduce respiratory drive, and the resultant CO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Monitor such patients for signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularly when initiating therapy with SEGLENTIS. Opioids may also obscure the clinical course in a patient with a head injury. Avoid the use of SEGLENTIS in patients with impaired consciousness or coma.
-
Risk of Use in Patients with GI Conditions: The tramadol in SEGLENTIS may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi. Opioids may cause increases in serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis, for worsening symptoms.
-
Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
-
Hepatotoxicity: As tramadol and celecoxib are both extensively metabolized by the liver, the use of SEGLENTIS in patients with moderate and severe hepatic impairment is not recommended. Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue SEGLENTIS immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient. Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity.
-
Hypertension: NSAIDs, including celecoxib, a component in SEGLENTIS, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazide diuretics or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
-
Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid the use of SEGLENTIS in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If SEGLENTIS is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
-
Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia: Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of an NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, dehydration, hypovolemia, heart failure, or liver dysfunction; those taking diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs); and the elderly. Increases in serum potassium concentration, including hyperkalemia, have been reported with use of NSAIDs, even in some patients without renal impairment.
-
Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: SEGLENTIS is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity).
-
Serious Skin Reactions: Serious skin reactions have occurred following treatment with celecoxib, a component of SEGLENTIS, including erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. These serious events may occur without warning and can be fatal. Discontinue SEGLENTIS at first appearance of skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity.
-
DRESS: Discontinue and evaluate clinically.
-
Fetal Toxicity: Limit use of NSAIDs, including SEGLENTIS, between about 20 to 30 weeks in pregnancy due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction. Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy due to the risks of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
-
Hematologic Toxicity: Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with SEGLENTIS has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit. NSAIDs, including SEGLENTIS, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders or concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), SSRIs, and SNRIs may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding.
-
Withdrawal: Do not abruptly discontinue SEGLENTIS in a patient physically dependent on opioids. When discontinuing SEGLENTIS in a physically dependent patient, gradually taper the dosage. Rapid tapering of tramadol in a patient physically dependent on opioids may lead to a withdrawal syndrome and return of pain. Additionally, avoid the use of mixed agonist/antagonist (e.g., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) or partial agonist (e.g., buprenorphine) analgesics in patients who are receiving a full opioid agonist analgesic, including SEGLENTIS. In these patients, mixed agonist/antagonist and partial agonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms.
-
Driving and Operating Machinery: SEGLENTIS may impair the mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating machinery. Warn patients not to drive or operate dangerous machinery unless they are tolerant to the effects of SEGLENTIS and know how they will react to the medication.
-
Masking of Inflammation and Fever: The pharmacological activity of SEGLENTIS in reducing inflammation, and possibly fever, may diminish the utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections.
-
Hyponatremia: Hyponatremia (serum sodium <135 mmol/L) has been reported with the use of tramadol, a component of SEGLENTIS, and many cases are severe (sodium level <120 mmol/L). Most cases of hyponatremia occurred in females over the age of 65 and within the first week of therapy. In some reports, hyponatremia resulted from the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hyponatremia (e.g., confusion, disorientation) during treatment with SEGLENTIS, especially during initiation of therapy. If signs and symptoms of hyponatremia are present, initiate appropriate treatment (e.g., fluid restriction) and discontinue SEGLENTIS.
-
Hypoglycemia: Cases of tramadol-associated hypoglycemia have been reported, some resulting in hospitalization. In most cases, patients had predisposing risk factors (e.g., diabetes). If hypoglycemia is suspected, monitor blood glucose levels and consider drug discontinuation as appropriate.
Adverse Reactions
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >5% and > placebo) for SEGLENTIS are nausea (30%), vomiting (16%), dizziness (17%), headache (12%), and somnolence (8%).
Select Drug Interactions
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist and Partial Agonist Opioid Analgesics: Avoid use with SEGLENTIS because they may reduce analgesic effect of SEGLENTIS or precipitate withdrawal symptoms.
Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking SEGLENTIS with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of SEGLENTIS and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended.
ACE Inhibitors, ARBs, or Beta Blockers: Concomitant use with SEGLENTIS may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure.
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with SEGLENTIS in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high-risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function.
Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects.
Digoxin: Concomitant use with SEGLENTIS can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels.
Drug Abuse and Dependence
SEGLENTIS contains tramadol, a Schedule IV controlled substance with a high potential for abuse similar to other opioids and can be abused and is subject to misuse, addiction, and criminal diversion. All patients treated with opioids require careful monitoring for signs of abuse and addiction, since use of opioid analgesic products carries the risk of addiction even under appropriate medical use. Careful record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests, as required by state and federal law, is strongly advised. Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs.
Physical dependence is a physiological state in which the body adapts to the drug after a period of regular exposure, resulting in withdrawal symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dosage reduction of a drug.
Overdosage
SEGLENTIS is a combination drug composed of tramadol and celecoxib. The clinical presentation of overdose may include the signs and symptoms of tramadol toxicity, celecoxib toxicity, or both.
Tramadol:
Acute overdosage with tramadol can be manifested by respiratory depression, somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, constricted pupils, and, in some cases, pulmonary edema, bradycardia, QT prolongation, hypotension, partial or complete airway obstruction, atypical snoring, seizures, and death. Marked mydriasis rather than miosis may be seen with hypoxia in overdose situations.
Deaths due to overdose have been reported with abuse and misuse of tramadol. Review of case reports has indicated that the risk of fatal overdose is further increased when tramadol is abused concurrently with alcohol or other CNS depressants, including other opioids.
Celecoxib:
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. GI bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare.
For more information on appropriate treatment of overdose with SEGLENTIS, see the full Prescribing Information.
Opioid Analgesic Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS)
To ensure that the benefits of opioid analgesics, including SEGLENTIS, outweigh the risks of addiction, abuse, and misuse, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has required a REMS for these products. Under the requirements of the REMS, drug companies with approved opioid analgesic products must make REMS-compliant education programs available to healthcare providers.
To obtain further information on the opioid analgesic REMS and for a list of accredited REMS continuing education, call 1-800-503-0784, or log on to www.opioidanalgesicrems.com.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Kowa Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. at 1-888-SEGLENTIS or the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
For additional information please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, and Medication Guide, for SEGLENTIS.
Intended for healthcare professionals of the United States of America only.